Serial Multiplier Vhdl Code
- Serial Multiplier Vhdl Code For Windows 7
- Serial Multiplier Vhdl Code Generator
- Booth Multiplier Vhdl Code
- 4 Bit Multiplier Vhdl Code
Introduction
- Inputs: A1, A0, B1, B0 : 2 bit

- 3 different VHDL implementations
- Synthesis “by hand” (boolean functions for the outputs)
Notes
VHDL code for register; How to read content from text file and How to writ. FPGA programming using System Generator; Versions of XILINX ISE design tools compatible wit. How to use black box xilinx blockset in system gen. VHDL code for 4 Bit multiplier using NAND gate; VHDL code for addition of 4BITADDER with user li. VHDL code for 4.
- Mar 28, 2020 In this article, we will be writing the VHDL code for a 2-bit binary multiplier using all the three modeling techniques. We will write the code, testbench and will also create the RTL schematics for the same.
- Search a vhdl code for 8 bit serial parallel binary multiplier, 300 result(s) found vhdl code for alu and detemines the basic components of alu unit in cpu system.
- I need a verilog code for serial multipler. Skills: FPGA, LabVIEW, Microcontroller, Software Architecture, Verilog / VHDL See more: serial multiplier pdf, verilog code for multiplication of two numbers, 4 bit multiplier verilog code, 8 bit multiplier verilog code, 16 bit multiplier verilog code, 8 bit array multiplier verilog code, serial multiplier block diagram, n bit multiplier verilog code.
Different VHDL coding styles shall be demonstrated with a simple module that has to calculate the result of the multiplication of two 2-bit numbers. The maximum value of each input is 3, i.e. the maximum output value is 9 which needs 4 bits in a binary code.
Therefore, four input ports and four output ports of data type ’bit’ are required. What is adobe typekit.
The same entity shall be used for all different implementations.
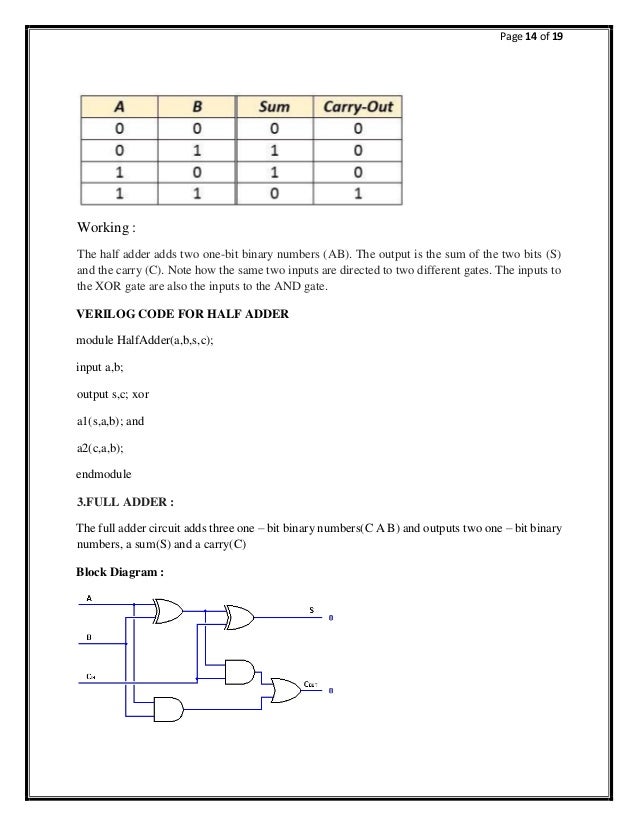
Mutliplier: Function Table
| a1 | a0 | b1 | b0 | c3 | c2 | c1 | c0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Notes
The most direct approach is via the function table of the multiplications. The behavior of a combinational logic block is completely defined by listing the result for all possible input values. Of course, the function table is usually no the most compact representation.
Multiplier Minterms - Karnaugh Diagram
Notes
The function table of this 2×2 bit multiplier leads directly to the four Karnaugh diagrams of the output signals.
The bars on the side of the squares indicate those regions where the corresponding input bit is ’1’.
All ’1’s of the output signals are marked in the corresponding diagrams. By combining adjacent ’1’s, the minimal output function can be derived.

Multiplier: VHDL Code using the Function Tables
- An internal signal is used that combines all input signals
- The internal signal is generated concurrently, i.e. it is updated whenever the input changes
- The function table is realized as case statement and thus has to placed within a process. The internal signal is the only signal that controls the behavior.

Notes
The conversion of the function table into VHDL is straight forward. An intermediate signal is used to combine the four input signals which facilitates the coding. Every row is represented by a different signal value, now. As all possibilities are covered in the table, a case structure can be used for the implementation.
Serial Multiplier Vhdl Code For Windows 7
Multiplier: VHDL Code using Minterm Functions
- The minterm functions are realized directly as concurrent statements
Notes
Because the minterms are rather simple logical functions, they are realized with concurrent statements. This way, it is just a matter of replacing the mathematical symbols with their corresponding VHDL operators.
The minterm realization is very tedious and is performed by the synthesis tool automatically when the function table is parsed.
It is more or less a structural implementation of the algorithm - no synthesis is required.
Multiplier: Integer Realization
- The NUMERIC_BIT package provides all necessary functions to convert bit vector to integer values and vice versa
- Internal signals are used to generate bit vectors and integer representations of the port signals. The bit vectors shall be treated as unsigned binary values.
- The signal bit input signals are concatenated to vectors and converted to integer data types
- the multiplication s realized via the standard VHDL operator
- The size of the target vector must be specified when converting integers back to bit vectors
- Finally, the bit vector elements are assigned to the output ports

Notes
Serial Multiplier Vhdl Code Generator
The most obvious solution via the multiplication operator ’*’ is not directly applicable because only single bits are provided by the entity.
Thus, bits belonging together are combined in bit vectors which are converted to integer values afterwards. The inverse procedure is necessary to assign the integer result to the output ports.
The most elegant solution is the integer implementation as the function of the code is clearly visible and not hidden in boolean functions or in hardcoded values like in the other examples. The use of ’bit’ type ports, however, is very awkward.
It is better style to use ’unsigned’ bit vectors or ’integer’. Please note that the conversion of the bit vectors to ’integer’ is not necessary as the arithmetic operators, including ’*’ are overloaded in the NUMERIC_BIT package. Vector arithmetic is provided for signed and unsigned binary representations
The synthesis result should be identical in all three cases. Colortone download free font.
Booth Multiplier Vhdl Code
Chapters of System Design > Synthesis > Combinational Logic
4 Bit Multiplier Vhdl Code
Chapters of System Design > Synthesis